What is Seed Phrase and How to Use It Securely
A cryptocurrency wallet is an endpoint to the world of blockchain and web3 technology. It permits crypto enthusiasts to save, send, receive, and (in some cases) exchange their assets with each other.
While crypto wallets unlock a plethora of new opportunities in terms of security, transparency, and censorship resistance, using them takes basic skills of crypto security and a high-level understanding of how blockchains work.
Read Also: Scam Alert: NFT Major OpenSea gets Its Main Discord Hacked
What are crypto wallets?
In general, a crypto wallet is a software mechanism designed for storage, sending, and exchanging cryptocurrency. At the same time, a crypto wallet is an address in the blockchain associated with this or that keypair (private and public key). Just like a bank account, every wallet has its balance, i.e., the number of units of this or that blockchain (BTC for Bitcoin, Ethers for Ethereum) stored on the wallet at the current block.
In the Blockchain world, to transact, an owner of a crypto wallet authorizes the transaction with his/her private key. After the transaction is authorized, cryptocurrency tokens are transferred from the balance of his/her account.
Although owing to the nature of blockchain technology, the tokens do not come to the receivers’ wallets in the instant.
The transaction is added to a queue (called “mempool”); the recipient’s wallet receives the coins with latency.
Unlike bank accounts, crypto wallets can be created in a few clicks in a zero-fee manner. Every user can create an unlimited number of wallets on every blockchain. Every crypto wallet has a unique address: for instance, a first-ever Bitcoin (BTC) wallet has a “Bitcoin genesis” address 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa. Bitcoin wallets’ addresses can start with 1, 3, or bc1. Ethereum (ETH) wallets start with 0x; the genesis wallet address includes 0x, followed by 40 zeroes. Also, crypto wallet addresses can be shared as QR codes.

What are public and private keys?
Public and private keys are two pivotal elements of crypto wallet cryptography (so-called public-key cryptography). The public key is known publicly; it serves as an identification number required to identify this or that wallet within the blockchain. Private keys, on the other hand, should be kept secret: blockchain users need them for encryption and authorization of transactions.
On most blockchains, wallet addresses represent the hashed form of the public key. The public key is a string of alphanumeric characters that looks like 2049 035D 01DD 1DF2 2F2F EC33 EFD6… and so on.
In blockchains, private keys can be compared to PINs or passwords from email and social media accounts. A private key is also a string of alphanumeric symbols that cannot be hacked—for instance, D778FC48C8A32440DC8D13487CA8117CAF665CAD412F1C6074ACB487721BBF54.
Both private and public keys are generated automatically: private keys are therefore used to let the blockchain know that this or that owner has the right to authorize transactions from a certain account.
It is impossible to derive a public key from a blockchain address and to derive a private key from a public key. Every public key has its corresponding private key.
Read Also: Here’s Who Is Behind Majority of NFT Hacks and How Much They Hold
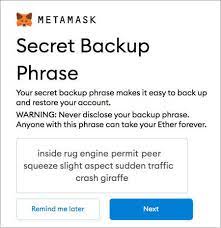
What is a seed phrase?
A seed phrase is a sort of nucleus of this or that crypto wallet. It includes all the information about the addresses associated with a blockchain wallet: its transaction details, balance, and so on.
Seed phrases consist of 12 English words: it is deduced randomly and used to restore a crypto wallet when the key pair is lost. In this case, it works like a key and lock in the same instance.

The order of words in seed phrases matters: when recovering a cryptocurrency wallet, you should enter them in the same order they were generated.
The wallet generates a seed phrase and displays it to the owner of the wallet. On major software and hardware wallets, one seed phrase is used to recover access from wallets on various blockchains, i.e., on Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Ethereum.
What’s the difference between custodial and noncustodial wallets?
As you may see, the management of private keys and seed phrases takes responsibility and basic technical skills. As blockchain adoption accelerates, some services started offering key management services.
Custodial wallets
Custodial (or “centralized”) cryptocurrency wallets can be accessed by a login/password pair just like email or a digital bank account on PayPal and Venmo. This means that they control your keys and seed phrases – or at least store “your” coins on their addresses in the blockchain.
Typically, such wallets are associated with large crypto ecosystems like Binance (BNB) or Coinbase. While using them, you can recover your wallet even without a seed phrase. Also, they are feature-rich: you can stake, exchange your tokens, trade with leverage, or withdraw to fiat accounts.
However, the “not your keys, not your coins” rule works perfectly for centralized exchanges. Their teams can easily freeze your funds. Also, due to FATF rules, using top-tier custodial wallets is impossible without passing KYC checks.
Noncustodial wallets
Users of noncustodial (“decentralized,” “self-custodial”) are solely responsible for the security and privacy checks. They can recover their wallets directly with seed phrases and private keys. Also, there is no need to register accounts and perform KYC checks.
Read Also: How to buy cryptocurrency
Although, if the seed phrase is lost, no one world be able to restore access to funds, they are gone forever. In that case, owners of noncustodial wallets should be super-cautious about key management and seed phrase security.
How to keep your seed phrase safe
At the same time, security management for noncustodial wallets (keeping seed phrases and private keys) relies on very simple rules.
Write it on the physical device
Do not skip this step: write a seed phrase on paper or a special metal plate (if you are using a sophisticated hardware wallet). Make some copies and keep all of them in secret places.
Avoid saving it on a PC
Do not save your seed phrase in iCloud, “Saved Messages” in messenger; avoid sending it to yourself via email. Modern malware can find them wherever they are stored in digital form.
Do not put all your eggs in one basket
As with asset management, consider building a “diversified portfolio” of crypto wallets. It is better to store money not only in different assets but also in different wallets, both centralized and decentralized.
Read Also: Cryptocurrency UPSC, crypto definition, advantages, and disadvantages.
Money loves silence
Last but not least, do not talk too much about your crypto assets and the ways you store them. Do not forget that every person interested in your seed phrase or private key on the internet is a scammer.
In conclusion, a seed phrase is an important instrument for recovering your assets from noncustodial wallets. It includes 12 English words put in a certain order.

Cryptolifedigital is a cryptocurrency blogger and analyst known for providing insightful analysis and commentary on the ever-changing digital currency landscape. With a keen eye for market trends and a deep understanding of blockchain technology, Cryptolifedigital helps readers navigate the complexities of the crypto world, making informed investment decisions. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, Cryptolifedigital’s analysis offers valuable insights into the world of cryptocurrency.




